ESG Investing using AI and Python for Beginners in Sustainable Finance
ESG investing (Environmental, Social, and Governance) has become the new norm as the world rushes towards sustainable and ethical investment practices.
This transition not only reflects a growing demand for corporate responsibility but also underscores the financial sector’s recognition of sustainability as a critical driver of long-term profitability.
Central to this shift is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Python, two powerful tools that are reshaping how investors analyze, select, and manage ESG investments.
So in this article I will show you how to use AI and Python in a practical way for ESG Investing.
The Rise of ESG Investing
ESG investing considers environmental, social, and governance factors alongside traditional financial metrics to evaluate the sustainability and ethical impact of an investment.
This approach is driven by the understanding that ESG factors can significantly affect a company’s performance, risk profile, and reputation.
The popularity of ESG investing has soared in recent years, with assets under management in ESG funds reaching unprecedented levels.
This surge reflects a growing consensus among investors that sustainable business practices are linked to long-term value creation.
ESG Investing using AI and Python — A Practical Application
Before moving further, for extracting the data, we’ll be using the APIs of FinancialModelingPrep.
So for the smooth execution of the upcoming code block, you need to have an FMP developer account which you can easily create using the link here.
Step 1: Setting Up
First, ensure you have requests installed for making API calls:
pip install requestsStep 2: Fetching ESG Data
We’ll write a Python script that uses the provided endpoints to fetch ESG data for AAPL, analyze its ratings, and compare it with sector benchmarks.
import requests
# Replace 'YOUR_API_KEY' with your actual FMP API key
api_key = 'YOUR_API_KEY'
# Define the base URL for FMP API
base_url = 'https://financialmodelingprep.com/api/v4'
# Endpoints
esg_data_endpoint = f"{base_url}/esg-environmental-social-governance-data?symbol=AAPL&apikey={api_key}"
esg_ratings_endpoint = f"{base_url}/esg-environmental-social-governance-data-ratings?symbol=AAPL&apikey={api_key}"
esg_benchmark_endpoint = f"{base_url}/esg-environmental-social-governance-sector-benchmark?year=2022&apikey={api_key}"
# Fetch ESG Data
esg_data_response = requests.get(esg_data_endpoint)
esg_ratings_response = requests.get(esg_ratings_endpoint)
esg_benchmark_response = requests.get(esg_benchmark_endpoint)
# Assuming the API returns JSON and the status codes are 200 for successful calls
if esg_data_response.status_code == 200 and esg_ratings_response.status_code == 200 and esg_benchmark_response.status_code == 200:
esg_data = esg_data_response.json()
esg_ratings = esg_ratings_response.json()
esg_benchmark = esg_benchmark_response.json()
# Example of processing the responses
print("ESG Data:", esg_data)
print("ESG Ratings:", esg_ratings)
print("ESG Benchmark:", esg_benchmark)
else:
print("Failed to fetch ESG data. Please check your API key and endpoints.")Step 3: Analysis and Visualization
After fetching the data, you could extend this script to analyze and visualize the ESG performance of AAPL. For instance, you might want to:
Calculate the average ESG score of AAPL compared to its sector benchmark.
Identify trends in AAPL’s ESG performance over time (assuming you fetch data across multiple years).
Use Python libraries like
matplotliborseabornfor visualizing AAPL’s ESG scores against its peers.
I will show you the code for the first one with mock-data.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Mock data from API responses (replace these with your actual API response data)
esg_data = {
'symbol': 'AAPL',
'esgScore': 75 # Hypothetical ESG score
}
esg_benchmark = {
'sector': 'Technology',
'averageEsgScore': 70 # Hypothetical average ESG score for the Technology sector
}
# Creating a DataFrame for visualization
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Category': ['AAPL ESG Score', 'Sector Average ESG Score'],
'Score': [esg_data['esgScore'], esg_benchmark['averageEsgScore']]
})
# Plotting
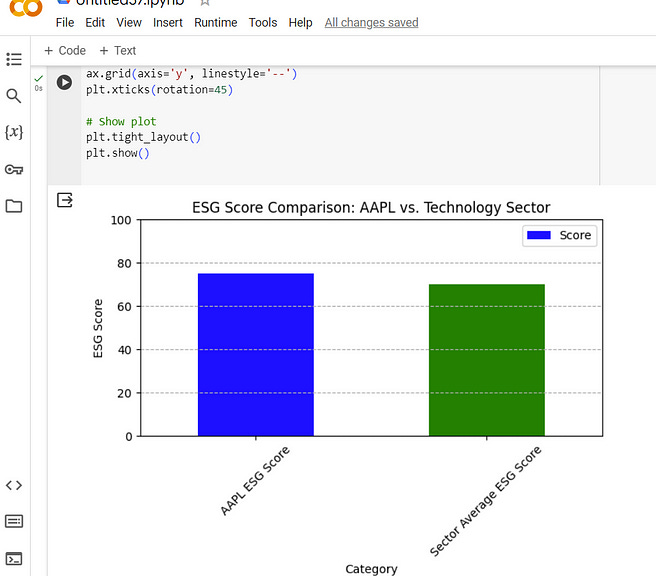
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
df.plot(kind='bar', x='Category', y='Score', ax=ax, color=['blue', 'green'])
# Customization for clarity
ax.set_ylabel('ESG Score')
ax.set_title('ESG Score Comparison: AAPL vs. Technology Sector')
ax.set_ylim(0, 100) # Assuming ESG scores range from 0 to 100
ax.grid(axis='y', linestyle='--')
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
# Show plot
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()The output would be:
Visualization plays a crucial role in ESG investing by providing clear, impactful insights into the sustainability performance of companies and sectors, thereby aiding investors in making informed decisions.
So I encourage you to also try other data visualizations techniques/methods in Python such as:
Trend Analysis: If you have historical ESG data for AAPL and its sector, you could plot a line graph showing trends over time.
Detailed Breakdown: For more detailed ESG ratings (e.g., environmental, social, governance scores separately), consider using a grouped bar chart or stacked bar chart for a comprehensive comparison.
Interactivity: Libraries like
PlotlyorBokehcan be used instead ofmatplotlibfor interactive visualizations that allow users to explore the data more deeply.
The Role of AI in ESG Investing
AI plays a pivotal role in ESG investing by enabling the analysis of vast datasets to identify trends, risks, and opportunities related to sustainability.
Traditional methods of ESG analysis often struggle to cope with the sheer volume and complexity of data, from corporate sustainability reports to social media sentiment. AI, particularly machine learning and natural language processing (NLP), can sift through this information, extracting valuable insights that inform investment decisions.
How to do it in Python?
Python, a versatile programming language, has emerged as a preferred tool for financial analysts and data scientists working in ESG investing.
Its simplicity, flexibility, and extensive ecosystem of libraries, such as Pandas for data manipulation, Matplotlib and Seaborn for data visualization, and Scikit-learn for machine learning, make Python ideally suited for ESG data analysis.
Python enables analysts to clean, process, and analyze ESG data efficiently, facilitating the development of sophisticated models that predict ESG performance and its impact on financial returns.
In a real-world scenario, you’d extract historical ESG scores and other relevant features (e.g., financial performance indicators, market sentiment scores from news articles) from your database or API responses.
For simplicity, we’ll create a mock dataset:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# Mock dataset: Historical ESG scores and a dummy feature (e.g., market sentiment score)
data = {
'Year': [2018, 2019, 2020, 2021, 2022],
'MarketSentimentScore': [0.65, 0.70, 0.68, 0.72, 0.75], # Hypothetical sentiment scores
'ESGScore': [65, 67, 70, 72, 75] # Hypothetical historical ESG scores
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Features and target variable
X = df[['MarketSentimentScore']] # Using market sentiment score as a feature
y = df['ESGScore'] # Target variable
# Splitting dataset into training and test sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)Building and Training the Model
We’ll use a simple linear regression model to predict the ESG score based on the market sentiment score:
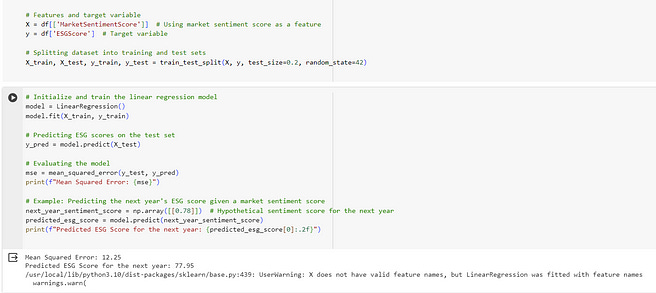
# Initialize and train the linear regression model
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predicting ESG scores on the test set
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Evaluating the model
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Mean Squared Error: {mse}")
# Example: Predicting the next year's ESG score given a market sentiment score
next_year_sentiment_score = np.array([[0.78]]) # Hypothetical sentiment score for the next year
predicted_esg_score = model.predict(next_year_sentiment_score)
print(f"Predicted ESG Score for the next year: {predicted_esg_score[0]:.2f}")The output would be:
Notes and Further Steps
Model Complexity: Linear regression is a very basic model. Depending on the complexity of your data and the accuracy required, you might explore more sophisticated models, such as Random Forests, Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM), or even Neural Networks for deeper insights. I wrote more articles on this:
Feature Engineering: The accuracy of your predictions heavily depends on the quality and relevance of the features used. Incorporating more relevant features, such as financial performance indicators, environmental impact metrics, and governance scores, could significantly improve your model’s predictive power.
Evaluation: It’s important to thoroughly evaluate your model using appropriate metrics and validation techniques. Beyond mean squared error (MSE), consider using R-squared, mean absolute error (MAE), and conducting cross-validation to assess model performance.
AI-Driven ESG Scoring Models
One of the most significant applications of AI in ESG investing is the development of ESG scoring models.
These models leverage AI algorithms to evaluate a company’s performance across various ESG criteria, assigning scores that help investors identify leaders and laggards in sustainability.
By training these models on historical data, AI can uncover patterns and correlations that human analysts might overlook, offering a more nuanced and comprehensive assessment of ESG risks and opportunities.
Python in Action: Building an ESG Analysis Tool
To illustrate the practical application of Python in ESG investing, consider the development of a simple ESG analysis tool.
This tool could use Python’s NLP libraries, such as NLTK or spaCy, to analyze the sentiment of news articles, reports, and social media posts related to a company’s ESG practices.
By aggregating this data and applying machine learning models, the tool could generate an ESG sentiment score, providing investors with a real-time gauge of a company’s ESG performance.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its potential, the integration of AI and Python in ESG investing faces challenges, including data quality and availability, model transparency, and the need for standardized ESG reporting frameworks.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation, as the finance sector seeks to refine data collection methods, develop more sophisticated AI models, and establish universal ESG standards.
Final Words
The fusion of AI and Python in ESG investing represents a transformative shift towards more sustainable and responsible finance. By leveraging these technologies, investors can gain deeper insights into the ESG performance of their portfolios, driving not only financial returns but also positive environmental and social outcomes.
As the field continues to evolve, the potential for AI and Python to contribute to a more sustainable future remains vast, promising a new era of investment that values not just profit, but the planet and people as well.